
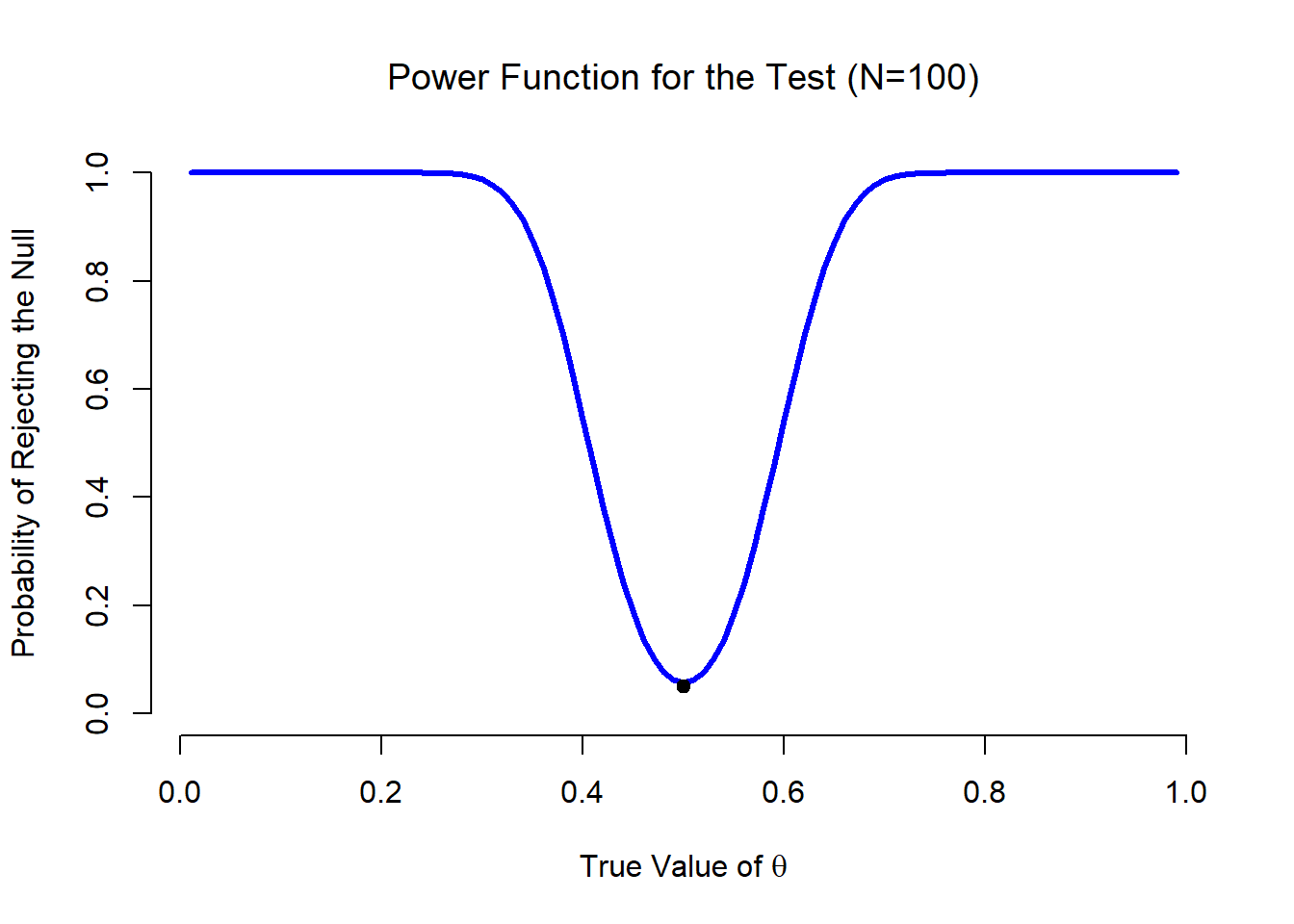
Binom(n(number of trials) ,p(probability of success) )ġ2. The number of trials n, and the probability of success p.īinomial Model. In the binomial distribution, what do parameters n and p represent?
How do you find the expected value and standard deviation of a binomial random variable?ġ0. Binomial setting has two parameters, number of trials and probability of success.ĩ. The geometric setting has one parameter, the probability of success.Ī binomial setting is used to measure the number of successes. Explain the difference between the binomial setting and the geometric setting.Ī geometric setting is used to see how long it will take to achieve a success. The variable of interest is the number of successesĨ. What is the variable of interest in a binomial model? A cumulative distribution function finds the sum of the probabilities of several possible outcomes.ħ. What is the difference between a probability distribution function (pdf) and a cumulative distribution function (cdf)?Ī probablility distribution function finds the probability of any individual outcome. If X has a geometric distribution, what does (1 – p)n – 1p represent?Ħ. P represents the probablity of success (q = 1 - p is probability of failure)ĥ. In the geometic distribution, what does the parameter p represent? Standard deviation = square root(q/(p squared)) where q = probability of failureĤ. How do you find the expected value and standard deviation of a geometric random variable?Įxpected value : mean = 1/p, where p = the probability of success (i.e., the Step by Step problem, How long will it take them to find someone with O negative blood?)ģ. The variable of interest in a geometric model is how long it will take to achieve success. What is the variable of interest in a geometric model? List three characteristics of Bernoulli trials.ġ.) There are only 2 possible outcomes on each trialĢ.) The probability of success is the same on every trialĢ. Known asīinomcdf(n,p,X), n stands for number of trials, p stands for probabilty, and X stands for number of successes from x number to 0.ġ. Known as binompdf(n,p,k), where n stands for number of trials, p stands for probability of success, and k is the desired number of successes.īinomcdf(-located under 2nd Dist and allows us to find the total probability of getting x or fewer successes among n trails. calculates the the probability of finding the first success on or before the xth trial.īinompdf(- located under 2nd Dist and allows us to find the probability of an individual outcome. Geometcdf(cumulative density function, finds the sum of the probabilities of several possible outcomes. When using, you put in geometpdf(probability, # of trials) Geometpdf( found under 2nd Dist, used to find the probability that it takes a certain number of trials to get a success. Geometric model- shows how long it takes to achieve a success.īinomial model- requires two parameters, Binom( n,p) Bernoulli trials- There are only 2 possible outcomes(success or failure), the probability of success is the same on each trial, and the trials are


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
